This document describes the details you need to know to extend/maintain XSOM.
The primary design goals of XSOM are:
Providing mutation methods was a non-goal for this project, primarily because of the added complexity.
The workspace uses Ant as the build tool. The followings are the major targets:
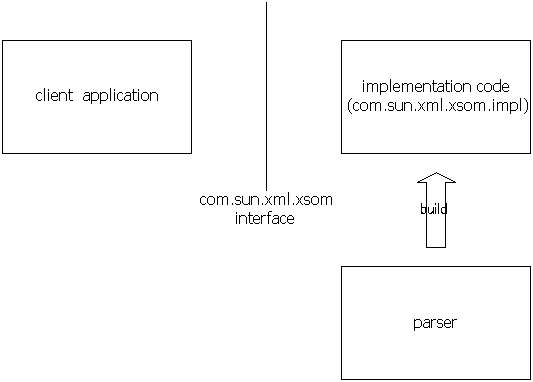
XSOM consists of roughly three parts.
The first part is the public interface, which is defined in the com.sun.xml.xsom package. The entire functionality of XSOM is exposed via this interface. This interface is derived from a draft document submitted to W3C by some WG members.
The second part is the implementation of these interfaces, the com.sun.xml.xsom.impl package. These code are all hand-written.
The third part is a parser that reads XML representation of XML Schema and builds XSOM nodes accordingly. The package is com.sun.xml.xsom.parser. This part of the code is mostly generated by RelaxNGCC.

Most of the implementation classes are fairly simple. Probably the only one interesting piece of code is the Ref class, which is a reference to other schema components.
The Ref class itself is just a place hodler and this class defined a series of inner interfaces that are specialized to hold a reference to different kinds of schema components.
The sole purpose of this indirection layer is to support forward references during a parsing of the XML representation.
A typical reference interface would look like this:
public static interface Term {
/** Obtains a reference as a term. */
XSTerm getTerm();
}
In case this indirection is unnecessary, all implementation classes of XSTerm implements this Ref.Term interface. This applies to all the other types of the Ref interface. Therefore, whereever a reference is necessary, you can stimply pass a real object. In other words, a direct reference (XS***Impl) can be always treated as an indirect reference (Ref.***).
Implementations for forward references are placed in the com.sun.xml.xsom.impl.parser.DelayedRef class. The detail will be discussed later.
The following collaboration diagram shows various objects that participate in a parsing process.
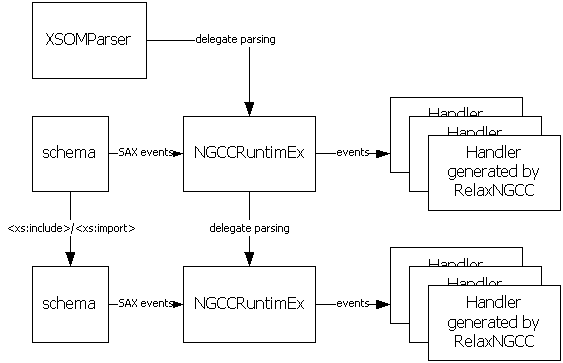
XSOMParser is the only publicly visible component in this picture. This class also keeps references to vairous other objects that are necessary to parse schemas. This includes an error handler, the root SchemaSet object, an entity resolver, etc.
Whenever the parse method is called, it will create a new NGCCRuntimeEx and configure XMLReader so that a schema file is parsed into this NGCCRuntimeEx instance.
NGCCRuntimeEx derives from NGCCRuntime, which is a class generated by RelaxNGCC. This object will use other RelaxNGCC-generated classes and parse a document and constructs a XSOM object graph appropriately.
When a new XML document is referenced by an import or include statement, a new set of NGCCRuntimeEx is set up to parse that document. One NGCCRuntimeEx can only parse one XML document.
Since we use SAX to parse schemas, the referenced schema component is often unavailable when we hit a reference. Because of this, when we see a reference, we create a "delayed" reference that keeps the name of the referenced component.
Note that because of the way XML Schema <redefine> works, all the references by name must be lazily bound even if the component is already defined.
All these "delayed" references are remembered and tracked by XSOMParser. When the client calls the XSOMParser.getResult method, XSOMParser will make sure that they resolve to a schema component correctly.
"Delayed" references are available in the DelayedRef class.
The actual parser is generated by RelaxNGCC from xsom/src/*.rng files. xmlschema.rng is the entry point and all the other files are referenced from this file. For more information about RelaxNGCC, goto here. Or just contact me (as I'm one of the developers of RelaxNGCC.)